Courtesy of NEI-online
What is AMD (Age-Related Macular Degeneration)?
黃斑部病變
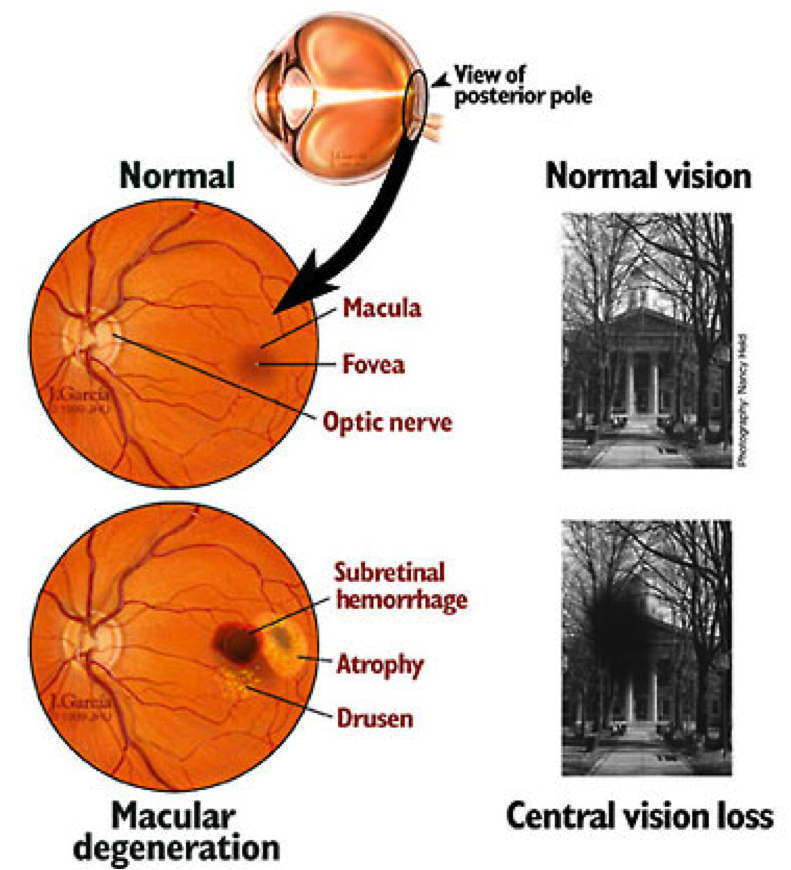
AMD is a common eye condition and a leading cause of vision loss among people age 50 and older. It causes damage to the macula, a small spot near the center of the retina and the part of the eye needed for sharp, central vision, which lets us see objects that are straight ahead.
In some people, AMD advances so slowly that vision loss does not occur for a long time. In others, especially the WET macular degeneration type, the disease progresses faster and may lead to a loss of vision in one or both eyes. As AMD progresses, a blurred, distorted area near the center of vision is a common symptom. Over time, the blurred area may grow larger or you may develop blank spots in your central vision. Objects also may not appear to be as bright as they used to be.
AMD by itself does not lead to complete blindness, with no ability to see. However, the loss of central vision in AMD can interfere with simple everyday activities, such as the ability to see faces, drive, read, write, or do close work, such as cooking or fixing things around the house.
Who is at risk?
Age is a major risk factor for AMD. The disease is most likely to occur after age 60, but it can occur earlier. Other risk factors for AMD include:
- Smoking. Research shows that smoking doubles the risk of AMD.
- Race. AMD is more common among Caucasians than among African-Americans or Hispanics/Latinos.
- Family history. People with a family history of AMD are at higher risk.
Does lifestyle make a difference?
Researchers have found links between AMD and some lifestyle choices, such as smoking. You might be able to reduce your risk of AMD or slow its progression by making these healthy choices:
- Avoid smoking
- Exercise regularly
- Maintain normal blood pressure and cholesterol levels
- Eat a healthy diet rich in green, leafy vegetables and fish
Not everyone with early AMD will develop late AMD. For people who have early AMD in one eye and no signs of AMD in the other eye, about 5% will develop advanced AMD after 10 years. For people who have early AMD in both eyes, about 14 % will develop late AMD in at least one eye after 10 years. With prompt detection of AMD, there are steps you can take to further reduce your risk of vision loss from late AMD.
If you have late AMD in one eye only, you may not notice any changes in your overall vision. With the other eye seeing clearly, you may still be able to drive, read, and see fine details. However, having late AMD in one eye means you are at increased risk for late AMD in your other eye. If you notice distortion or blurred vision, even if it doesn’t have much effect on your daily life, consult an eye care professional.
How is AMD treated?
It is important to monitor your symptoms monocularly, meaning that you close one eye and pay attention to the central vision in the other eye. It is also important to follow-up with your ophthalmologist.
Early AMD
Currently, no treatment exists for early AMD, which in many people shows no symptoms or loss of vision. Your eye care professional may recommend that you get a comprehensive dilated eye exam at least once a year. The exam will help determine if your condition is advancing.
As for prevention, AMD occurs less often in people who exercise, avoid smoking, and eat nutritious foods including green leafy vegetables and fish. If you already have AMD, adopting some of these habits may help you keep your vision longer.
Intermediate and late AMD
Researchers at the National Eye Institute tested whether taking nutritional supplements could protect against AMD in the Age-Related Eye Disease Studies (AREDS and AREDS2). They found that daily intake of certain high-dose vitamins and minerals can slow progression of the disease in people who have intermediate AMD, and those who have late AMD in one eye.
The first AREDS trial showed that a combination of vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, zinc, and copper can reduce the risk of late AMD by 25 percent. The AREDS2 trial tested whether this formulation could be improved by adding lutein, zeaxanthin or omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are nutrients enriched in fish oils. Lutein, zeaxanthin and beta-carotene all belong to the same family of vitamins, and are abundant in green leafy vegetables.
The AREDS2 trial found that adding lutein and zeaxanthin or omega-three fatty acids to the original AREDS formulation (with beta-carotene) had no overall effect on the risk of late AMD. However, the trial also found that replacing beta-carotene with a 5-to-1 mixture of lutein and zeaxanthin may help further reduce the risk of late AMD. Moreover, while beta-carotene has been linked to an increased risk of lung cancer in current and former smokers, lutein and zeaxanthin appear to be safe regardless of smoking status. If you have kidney or liver disease, it is prudent to inform your primary care physicians or nephrologists that you are taking the vitamins.
Here are the clinically effective doses tested in AREDS and AREDS2:
- 500 milligrams (mg) of vitamin C
- 400 international units of vitamin E
- 80 mg zinc as zinc oxide (25 mg in AREDS2)
- 2 mg copper as cupric oxide
- 15 mg beta-carotene, OR 10 mg lutein and 2 mg zeaxanthin
A number of manufacturers offer nutritional supplements that were formulated based on these studies. The label may refer to "AREDS" or "AREDS2."
If you have intermediate or late AMD, you might benefit from taking such supplements. But first, be sure to review and compare the labels. Many of the supplements have different ingredients, or different doses, from those tested in the AREDS trials. Also, consult your doctor or eye care professional about which supplement, if any, is right for you. For example, if you smoke regularly, or used to, your doctor may recommend that you avoid supplements containing beta-carotene.
Even if you take a daily multivitamin, you should consider taking an AREDS supplement if you are at risk for late AMD. The formulations tested in the AREDS trials contain much higher doses of vitamins and minerals than what is found in multivitamins. Tell your doctor or eye care professional about any multivitamins you are taking when you are discussing possible AREDS formulations.
Finally, remember that the AREDS formulation is not a cure. It does not help people with early AMD, and will not restore vision already lost from AMD. But it may delay the onset of late AMD. It also may help slow vision loss in people who already have late AMD.
Advanced neovascular AMD
Neovascular AMD typically results in severe vision loss. However, eye care professionals can try different therapies to stop further vision loss. You should remember that the therapies described below are not a cure. The condition may progress even with treatment.
- Injections. One option to slow the progression of neovascular AMD is to inject drugs into the eye. With neovascular AMD, abnormally high levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are secreted in your eyes. VEGF is a protein that promotes the growth of new abnormal blood vessels. Anti-VEGF injection therapy blocks this growth. If you get this treatment, you may need multiple monthly injections. Before each injection, your eye will be numbed and cleaned with antiseptics. To further reduce the risk of infection, you may be prescribed antibiotic drops. A few different anti-VEGF drugs are available. They vary in cost and in how often they need to be injected, so you may wish to discuss these issues with your eye care professional.
- Photodynamic therapy. This technique involves laser treatment of select areas of the retina. First, a drug called verteporfin will be injected into a vein in your arm. The drug travels through the blood vessels in your body, and is absorbed by new, growing blood vessels. Your eye care professional then shines a laser beam into your eye to activate the drug in the new abnormal blood vessels, while sparing normal ones. Once activated, the drug closes off the new blood vessels, slows their growth, and slows the rate of vision loss. This procedure is less common than anti-VEGF injections, and is often used in combination with them for specific types of neovascular AMD.
- Laser surgery. Eye care professionals treat certain cases of neovascular AMD with laser surgery, though this is less common than other treatments. It involves aiming an intense "hot" laser at the abnormal blood vessels in your eyes to destroy them. This laser is not the same one used in photodynamic therapy which may be referred to as a "cold" laser. This treatment is more likely to be used when blood vessel growth is limited to a compact area in your eye, away from the center of the macula, that can be easily targeted with the laser. Even so, laser treatment also may destroy some surrounding healthy tissue. This often results in a small blind spot where the laser has scarred the retina. In some cases, vision immediately after the surgery may be worse than it was before. But the surgery may also help prevent more severe vision loss from occurring years later.
Macular drusens and RPE detachment and subsequent distortions in the vision
WET AMD with large hemorrhagic retinal area and scotoma in the vision